Contents
The electric vehicle revolution is swiftly transforming the way we move. As electric vehicles gain popularity, the need for a standardized charging connector becomes increasingly crucial. Enter the SAE J1772 connector, developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers. With its unique design, the J1772 connector serves as a universal interface, allowing electric vehicles to connect seamlessly with charging stations. This standardized connection method facilitates convenience and compatibility, enabling EV owners to charge their vehicles at public stations, workplaces, and even in residential settings.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore every aspect of the J1772 connector, from its design to its impact on electric vehicle charging. Buckle up, as we uncover the power of the J1772 connector.
What is J1772?
The SAE J1772 connector, commonly referred to as a J plug or Type 1 connector, serves as the critical, universal link between electric vehicles and the EV charging infrastructure in North America. It provides a reliable, safe, and efficient charging interface for electric vehicles. The J1772 connector has been widely adopted in North America, with many automakers using J1772 plugs on their electric vehicles. With the exception of Tesla charging stations, all Level 1 and Level 2 charging stations in North America utilize the J1772 plug.
Due to its broad acceptance as the standard, most EV models manufactured for the North American market come equipped with a built-in J1772-compliant inlet, enabling them to connect to any charging station that uses the J1772 connector. In the case of Tesla, each vehicle delivery includes a J1772 adapter that can connect Tesla's proprietary charging port to most North American EV charging stations.
When the J1772 connector was first developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), its main objective was to establish a universal charging standard for electric vehicles (EVs). The SAE J1772 connector history dates back to 2001 with its adoption by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) as the initial standard for electric vehicle (EV) charging. Avcon introduced a rectangular connector at that time, capable of supporting 6.6 kW power delivery. Fast forward to 2008, and CARB proposed an upgraded design by Yazaki, which could handle up to 19.2 kW of power. This new connector, known as SAE J1772-2009, garnered significant support within the industry and was subsequently integrated into the international IEC 62196-2 standard.
Acknowledged as a "Type 1" implementation, SAE J1772-2009 continues to play a vital role in the EV charging infrastructure today. J1772 is primarily used for Level 1 and Level 2 charging, which are the most common types of charging for residential and commercial applications.
In 2011, SAE developed the J1772/CCS Combo Coupler as an extension of the SAE J1772-2009 connector to support fast DC charging. This innovation allowed for high-speed charging at up to 350 kW. It revolutionized EV charging technology, providing EV owners with a faster and more convenient charging experience. The J1772/CCS Combo Coupler has since gained widespread adoption, representing a significant advancement towards a sustainable and efficient transportation future.
J1772 Physical Layout and Pin Configuration
The J1772 connector, also known as a J plug or Type 1 connector, follows a standardized physical layout and pin configuration. The J1772 connector features a five-pin configuration, allowing for communication and power transfer between the electric vehicle and the charging station.
Let's explore the pin layout of the SAE J1772-2009 connector:
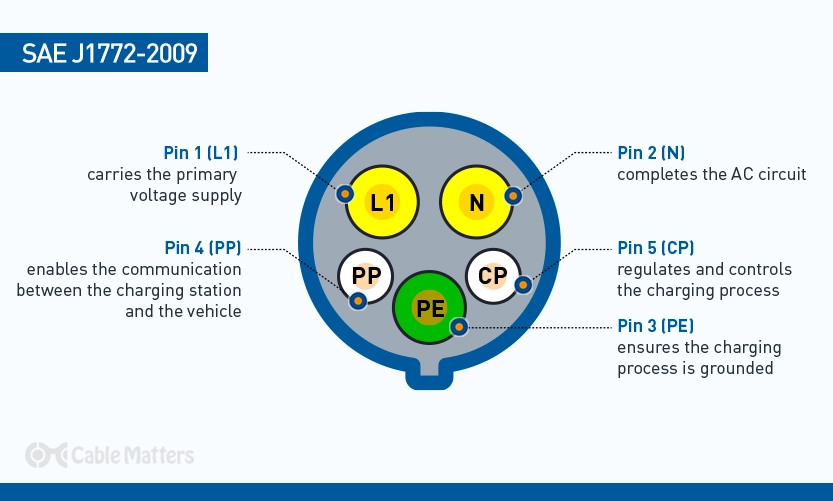
Pin 1: The Line 1 (L1) pin is responsible for carrying the primary voltage supply to the electric vehicle's onboard charger, enabling it to convert the AC power to DC power needed to charge the battery.
Pin 2: The Neutral (N) pin completes the AC circuit, allowing for the return of current to the charging source.
Pin 3: The Protective Earth (PE) pin is a safety feature that ensures the charging process is grounded, preventing electrical shock.
Pin 4: The Proximity Pilot (PP) pin is a communication pin that sends signals between the charging station and the vehicle, enabling it to communicate its charging capabilities and initiate the charging process.
Pin 5: The Control Pilot (CP) pin is a bi-directional communication pin that ensures the charging process is regulated and controlled. It allows the vehicle to send signals to the charging station, requesting certain charging currents and voltages and receives signals back from the charging station, informing the vehicle about the status of the charging process.
The J1772/CCS Combo Coupler, also known as Combined Charging Standard 1 (CCS1), combines the above 5-pin J1772 connector with two additional high-current pins that enable efficient DC charging.
This standardized layout and pin configuration enables interoperability between electric vehicles and charging stations compliant with the J1772 standard, providing a consistent charging experience for EV users. The future of EV charging looks bright, and the J1772 connector will undoubtedly continue to play a vital part in this exciting technological shift towards a cleaner, greener future.
J1772 vs. Other Charging Standards
The J1772 connector is widely embraced within the EV community, with Level 1 and Level 2 charging stations primarily utilizing this standard in North America. However, the Tesla Supercharger offers a proprietary connector that enables much faster charging speeds for Tesla vehicles. This specialized connector is designed exclusively for Tesla use, making it incompatible with other EV models. CHAdeMO, in contrast, is popular in Japan and Europe and offers high-power direct current (DC) fast charging capabilities. The CCS1 is a newer standard that combines a modified J1772 connector with additional pins for DC fast charging, enabling compatibility with both types of charging.
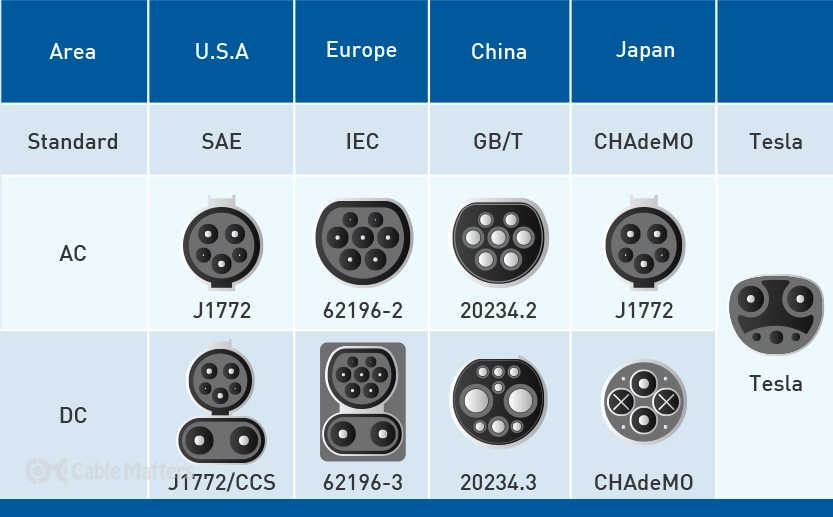
When it comes to J1772 versus other standards, each has its advantages and disadvantages. The J1772 connector's AC charging capability is well-suited to Level 1 and Level 2 charging, whereas the Tesla Supercharger is ideal for Tesla owners seeking faster charging speeds. CHAdeMO's high-power DC fast charging is a game-changer for vehicles that support it, and the CCS1's DC fast charging is a welcome addition for EVs that were originally designed to only support AC charging.
In terms of compatibility, J1772 adapters are readily available and can allow vehicles equipped with other connectors to use J1772 charging stations. Tesla also offers adapters that enable their vehicles to use J1772 charging stations. CHAdeMO and CCS1 adapters are also available, but their adoption and usage are not as widespread.
Ultimately, the industry is working towards universal standards and interoperability to create a cohesive and accessible charging infrastructure for all EV owners. While the benefits and trade-offs of different charging standards may vary, the continued advancement and adoption of electric vehicle technology ensures that more efficient and effective charging options will continue to emerge, enabling a brighter future for electric transportation.
Level 1 vs. Level 2 vs. DC Fast Charging
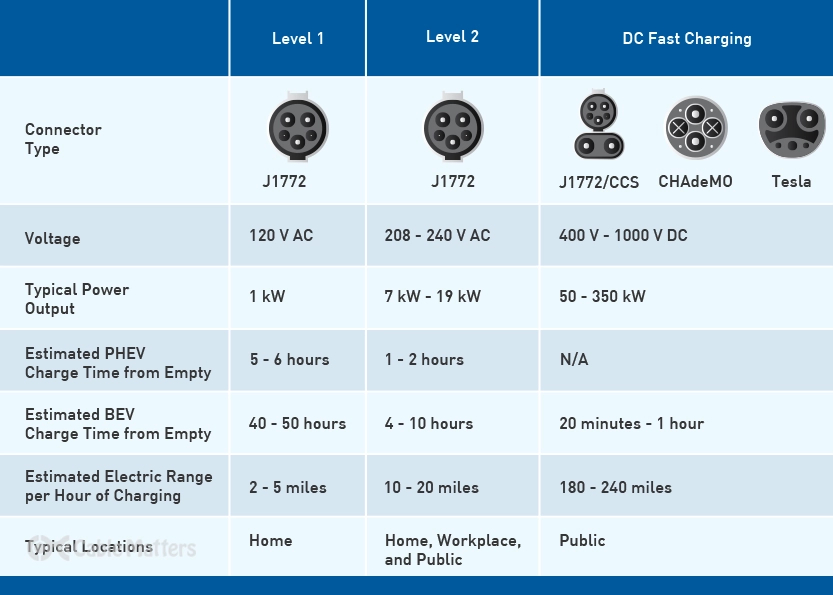
When it comes to charging your electric vehicle (EV), understanding the different levels of charging is crucial. Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging offer varying degrees of charging speed and compatibility, allowing you to choose the most suitable option based on your needs and available infrastructure.
Level 1 charging operates at 120 volts AC and is typically done using a standard household outlet. This is the slowest form of charging and is best suited for overnight charging or situations where time is not a constraint. It provides an average charging rate of 4-5 miles of range per hour, making it practical for daily commuting and shorter trips.
Moving up to Level 2 charging, we enter a faster charging realm. Level 2 charging requires a 240-volt AC power source, which can be installed at home or found at public and workplace charging stations. These charging stations are equipped with specialized connectors, such as the widely adopted J1772 connector. Level 2 charging provides an average charging rate of 25-30 miles of range per hour, significantly faster than Level 1 charging. This makes Level 2 charging ideal for those who need to replenish their EV's battery within a few hours, such as during the workday or overnight.
When it comes to long-distance travel or the need for rapid recharging, DC Fast Charging provides the highest charging speeds. DC Fast Charging stations supply direct current power to the vehicle, bypassing the vehicle's onboard charger. This allows for significantly faster charging rates, typically providing 80% or more of the battery's capacity within 30 minutes to an hour. DC Fast Charging stations utilize connectors such as CHAdeMO or CCS (Combined Charging System), depending on the vehicle and charging infrastructure. DC Fast Charging is ideal for road trips or situations where time is critical and requires access to dedicated high-power charging stations.
It's important to note that while Level 1 and Level 2 charging is widely adopted and compatible with most EVs, DC Fast Charging compatibility varies among vehicles. Not all EVs support DC Fast Charging, and even among those that do, different connector standards may require adapters or specific charging stations.
As the EV charging infrastructure continues to expand and evolve, Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging options offer flexibility and convenience for a wide range of EV owners. Whether you're looking for overnight charging, faster top-ups during the day, or rapid recharging on long trips, the growing availability of charging stations and emerging technologies ensure that electric vehicles remain a reliable and practical mode of transportation for the future.
Where To Find J1772 Charging Stations
As the popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) continues to rise, finding convenient and accessible charging stations is crucial for EV owners. When it comes to locating J1772 charging stations, you have a few reliable options at your disposal.
One of the most useful resources is the ChargeHub charging stations map. This comprehensive map provides an extensive database of public charging stations for EVs, including those equipped with J1772 connectors. With just a few clicks, you can easily find available charging stations near your location, ensuring that you have the necessary information to plan your charging needs effectively.
What sets ChargeHub apart is the wealth of detailed information it offers about each charging station. Along with the location, you can find crucial details such as the charging rate, connector type, and pricing. This makes it easier for EV owners to make informed decisions and select the most suitable charging station based on their requirements.
In addition to ChargeHub, it's worth checking with popular EV charging network providers like Blink or ChargePoint. These providers often have their own charging station maps and applications that go beyond merely indicating the location of J1772 charging stations. Their platforms provide real-time availability updates and vital station status information, ensuring that you can access up-to-date details about the charging stations in your vicinity.
With the help of these resources, the task of finding J1772 charging stations becomes seamless and convenient. The combination of detailed information, real-time updates, and easy-to-use interfaces empowers EV owners to navigate the charging infrastructure confidently.
Looking ahead, advancements in charging infrastructure and the continued collaboration between charging network providers, automakers, and governments promise an even more robust and efficient network of J1772 charging stations. As the demand for EVs continues to grow, the availability and accessibility of charging stations will only improve, bolstering the adoption and usability of electric vehicles for the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the SAE J1772 connector has played a vital role in the electric vehicle (EV) revolution, providing a standardized and universal charging interface for EVs in North America. With its unique design and compatibility with Level 1 and Level 2 charging stations, the J1772 connector has facilitated widespread convenience and accessibility for EV owners. The introduction of the J1772/CCS Combo Coupler has revolutionized fast DC charging, bringing faster and more convenient charging options to EV owners.
The physical layout and pin configuration of the J1772 connector, along with its interoperability with various EV models, ensure a safe and reliable charging experience. While other charging standards such as Tesla Supercharger and CHAdeMO offer their own advantages, the J1772 connector remains the standard choice for Level 1 and Level 2 charging in North America.
As the demand for EVs continues to rise, the availability and accessibility of J1772 charging stations will only improve. With resources like ChargeHub and EV charging network providers, finding J1772 charging stations has become easier than ever. The cooperation between charging network providers, automakers, and governments promises a brighter future for electric transportation, with an increasingly robust and efficient network of J1772 charging stations.
The J1772 connector has not only provided a crucial link between EVs and the North American EV charging infrastructure, but it has also paved the way for a more sustainable and efficient transportation future. With the ongoing advancements in EV technology and charging infrastructure, electric vehicles are set to become an even more practical and accessible option for transportation, making the J1772 connector a cornerstone of this exciting technological shift.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is J1772?
J1772 is a North American standard developed for electric vehicle charging ports. It refers to the plug and socket that connects an electric vehicle to a charging station.
How fast can J1772 charge an electric vehicle?
The charging rate for J1772 varies depending on the specific electric vehicle and the level of charging station used. Typically, J1772 charging stations in the United States provide up to level 2 charging, which can deliver up to 80 amps at 240 volts and charge an electric vehicle in 4-8 hours.
Are J1772 connectors compatible with all electric vehicles?
J1772 connectors are compatible with most electric vehicles, though some older vehicles may require an adaptor. Some electric vehicles may use different types of connectors, such as the Tesla Supercharger or the CHAdeMO connector.
What is the difference between a J1772 charging station and a Tesla Supercharger?
The main difference between J1772 charging stations and Tesla Superchargers is that the latter is designed solely for Tesla electric vehicles, while the former can charge most electric vehicles with a J1772 connector. Additionally, Tesla Superchargers can deliver much faster charging rates than standard J1772 charging stations.
Can J1772 charging stations be used for home charging?
Yes, J1772 charging stations can be used for home charging, although they may require installation by a licensed electrician.
Can J1772 charging stations be installed outdoors?
Yes, J1772 charging stations can be installed outdoors, provided they meet appropriate safety and weather protection guidelines.