
Navigation
Navigating through the myriad of Ethernet cable types and connectivity options can often seem daunting, especially when setting up a network for optimal performance. Among the most common questions that arise in this realm are the differences between various cable categories like CAT5 and CAT6, the usage of RJ45 connectors, and the choice between wired and wireless options such as WiFi. This article aims to shed light on these topics, demystifying the technical specifications and providing clear answers to frequently asked questions regarding CAT6 cables.
Whether you're setting up a home network, upgrading your business infrastructure, or simply looking to understand the benefits of CAT6 over its predecessors and wireless connections, this guide will serve as your comprehensive resource. Let's dive into the world of CAT6 and explore how it compares to other networking standards, ensuring you have all the necessary information to make informed decisions about your networking needs.
What is CAT6?
Category 6, better known as CAT6, represented a significant advancement in the Ethernet cabling industry when it was developed in 2002. Introduced to address the needs of modern networking environments, CAT6 was designed to facilitate faster data transmission speeds, minimize crosstalk (the transmission of signals between adjacent wires), and provide a robust solution for both residential and commercial network setups.
At its core, CAT6 includes four pairs of copper wire, much like its predecessor CAT5e, but it differs significantly in its capacity for performance. Where CAT5e cables provide up to 1 gigabit per second (Gbps) performance, CAT6 cables are engineered to operate at double that capacity, reaching speeds up to 2 Gbps under ideal conditions. When considering the operation of networks over longer distances, CAT6 maintains a higher quality of connection, supporting 10 Gbps speeds up to 55 meters compared to CAT5e’s markedly reduced efficiency over similar stretches.
The physical differences don’t end with the internal wiring. CAT6 cables are often better shielded than their earlier counterparts, a feature that translates to significantly reduced crosstalk and better overall network performance. This shielding varies, with some CAT6 cables incorporating a central spine that helps to reduce crosstalk further.
As a result of these advancements, CAT6 has become a popular choice for a range of applications. It is favored for professional data centers, office buildings, and other environments where high-speed internet service is critical. Moreover, as smart home technologies and other internet-dependent devices become more common, CAT6 is increasingly recommended for residential installations to future-proof home networks.
CAT6: Features and Specifications
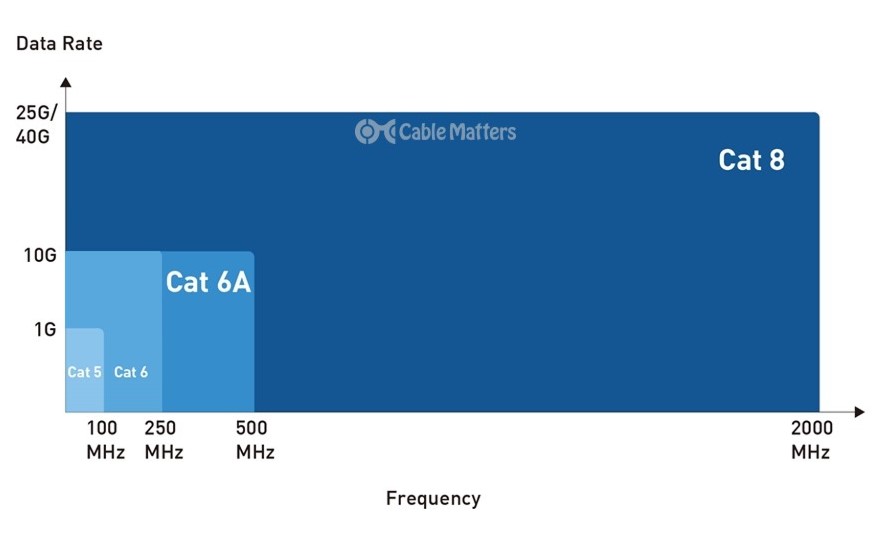
Delving deeper into CAT6’s features and specifications reveals why it has become the go-to choice for networking needs. Beyond the basic capability of supporting data rates of 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps and maintaining these speeds over up to 55 meters, CAT6 cables are engineered to operate efficiently at a frequency of up to 250 MHz—twice that of CAT5e cables. This enhanced frequency capability is key to supporting faster data transmission and accommodating bandwidth-intensive applications without degradation in signal quality.
The specifications for CAT6 cables are not merely about speed and frequency; they also encompass stricter physical construction standards. The tighter winding of CAT6’s copper wires and the optional use of plastic cross-separation within the cabling work together to minimize internal crosstalk. Furthermore, to combat external interference, some CAT6 cables feature improved shielding around the wires or even individual pairs, an aspect that becomes crucial in environments with significant electromagnetic interference.
Considering these enhanced performance specifications, it’s no wonder CAT6 is recommended for applications where network reliability, speed, and bandwidth are critical. From professional data centers requiring the utmost in data transfer efficiency and reliability to commercial installations where network performance can impact business operations, CAT6 provides a future-proof solution.
Additionally, for residential users, the difference made by CAT6 can be noticeable in everyday internet use. With the increasing presence of high-definition streaming services, gaming, and smart home devices—all of which demand robust and speedy connections—CAT6 offers a significantly improved user experience compared to older cable categories.
CAT6 vs. CAT6a
In the landscape of Ethernet cabling, the distinction between CAT6 and CAT6a is critical for those looking to optimize network performance. CAT6a, or Category 6 augmented, represents an evolution of the CAT6 standard, offering enhanced capabilities designed to meet the demands of high-speed networks more effectively.
One of the most significant upgrades CAT6a brings to the table is its doubling of operational frequency to 500 MHz, compared to CAT6's 250 MHz. This increase permits more robust data transfer rates and extends the cable's maximum effective distance for 10 Gbps networking to 100 meters, without sacrificing speed or reliability. Such attributes make CAT6a an ideal candidate for expansive network settings where both distance and data integrity are paramount.
Addressing the challenges of electromagnetic interference (EMI), CAT6a introduces more stringent specifications for crosstalk and noise suppression. This is achieved through the use of thicker wire gauges and enhanced shielding techniques, such as S/FTP or F/UTP, which encase individual wire pairs or the entire cable, respectively. These improvements significantly mitigate potential signal degradation due to external noise, thus ensuring a clearer signal transmission across the network.
However, the benefits of CAT6a come with certain considerations, notably in installation. The cable's increased diameter and stiffness might pose challenges in tight conduits or crowded cable paths, potentially impacting installation logistics and costs.
Despite these installation nuances, opting for CAT6a could be considered a strategic network infrastructure investment. Its superior performance not only caters to today's high-speed connectivity demands but also positions networks to seamlessly accommodate future technological advancements. Therefore, for enterprises that anticipate growth in bandwidth needs or operate in EMI-prone environments, CAT6a presents a future-proof solution that balances current performance requirements with long-term scalability.
CAT5 vs. CAT6
The differences between CAT5 and CAT6 Ethernet cables are substantial, with CAT6 outpacing CAT5 cables in various performance parameters. A highlight of CAT6 cables includes their provision of greater bandwidth, faster data transfer rates, and better handling of crosstalk and interference.
Though originally designed in the mid-90s, CAT5 cables, specifically the later variant CAT5e (Category 5 Enhanced), continued to be employed in many networking contexts for their straightforwardness and cost-effectiveness. They had adequate specifications for many personal and small business networks—supporting frequencies up to 100 MHz and data transfer speeds up to 1 Gbps over 100 meters.
However, as the demands on networks have grown in speed and complexity—supported by developments such as high-definition streaming, online gaming, cloud technology, and complex data transfers—the capabilities of CAT5e cables have increasingly struggled to meet users' needs. This is where CAT6 cables make their mark.
CAT6 cables double the bandwidth of CAT5e, supporting frequencies up to 250 MHz. When it comes to data transfer speeds, CAT6 does not necessarily increase the rate (still offering 1 Gbps over 100 meters), but where CAT6 truly shines is in its capacity to handle 10 Gbps over shorter distances (up to 55 meters), a feat CAT5e cannot accomplish.
Besides, CAT6 presents tighter specifications for cross-talk reduction. Significantly, CAT6 cables often feature more substantial shielding and tight twisting of the internal pairs of wires, minimizing interference from both within the cable (crosstalk) and from external sources.
Given the advancements CAT6 brings, it offers benefits for any networking environment. Its superior performance in high-demand applications, resistance to interference, and increasing affordability make it an attractive upgrade option even for smaller-scale or home networks.
CAT6: Applications & Use Cases
CAT6 cables have seen wide adoption in diverse industries due to their performance capabilities. Let's discuss the areas where CAT6 shines in particular because of its unique features and specifications.
One of the most notable applications for CAT6 cabling is in data centers. These demanding environments require high-speed data transfer and reliable connections to support immense amounts of data traveling between servers and endpoints. With its ability to handle 10 Gbps up to 55 meters and 1 Gbps over longer distances (up to 100 meters), CAT6 is an excellent choice for these applications. Its shielding mechanisms also help ensure reliable performance in an environment often packed with numerous signal sources.
Beyond data centers, CAT6 is prevalent in office environments. With businesses relying heavily on digital technologies, having a network infrastructure that supports high-speed, high-bandwidth, and high-reliability connections is non-negotiable. Whether it’s to support VoIP telephony, cloud services, large-scale file transfers, or conferencing platforms, CAT6 is the standard for new installations.
Enabled by its high-frequency abilities, CAT6 is also gaining traction in audio and video applications. It can support IPTV, video conferencing, and other streaming media services, providing clear, lag-free delivery.
For residential use, CAT6 is becoming increasingly popular for modern home networks. Its ability to support superior data speeds and minimize interference is crucial with the rise of smart home technologies, HD and 4K streaming, online gaming, and working or learning-from-home scenarios.
Conclusion
CAT6 represents a significant leap in Ethernet cabling standards. Designed for today’s high-speed, high-data network environments, CAT6 offers greater bandwidth and faster data transfer rates than CAT5e for a marginally higher cost.
But CAT6 cables don’t just promise better speed and bandwidth. They are robustly constructed to reduce signal interference—both from within the cable and from other sources in the environment. This makes them an attractive choice for data-heavy businesses and individuals alike, offering reliable connections that can handle the demands of modern apps and devices.
Choosing to invest in CAT6 cabling can thus provide significant long-term benefits. Such an investment ensures a network of future-proofed infrastructure, able to accommodate the continued growth in demand for bandwidth and speed in the digital era. Whether you're a large enterprise, a small business, or looking to optimize your home network, CAT6 cables should be the go-to choice for your networking needs.
CAT6 FAQ
Can I plug a Cat6 cable into a Cat5 jack?
Absolutely. CAT6 cables are backward compatible. This means that even though CAT6 cables are equipped to handle higher speeds and volumes of data, they can be plugged into older CAT5 or CAT5e jacks and ports. But remember, the speed at which data can be transferred will be limited to the capabilities of the slower CAT5/CAT5e components in such cases.
Is Cat5 faster than Cat6?
No. CAT6 surpasses CAT5e in terms of both data transfer speed and its frequency rate. While CAT5e can support speeds up to 1 Gbps at a frequency of 100 MHz, CAT6 can support 1 Gbps at a frequency double that of CAT5e (250 MHz). Moreover, unlike CAT5e, CAT6 can manage 10 Gbps speeds at shorter distances.
Is Cat6 better than WiFi?
CAT6 provides a faster, more stable, and secure connection than WiFi. Wired connections like CAT6 allow for higher-speed data transfers, fewer interruptions from interference, and added security that WiFi cannot match. However, the convenience and flexibility of a wireless WiFi connection make it the preferred option for devices like smartphones and tablets. For tasks that require high-speed, reliable connections—such as gaming, streaming in HD/4K, or big data transfers—CAT6 is often the better choice.
What is the difference between RJ45 and Cat6?
RJ45 and CAT6 refer to different aspects of networking. RJ45 is a type of connector that is used to connect a networking cable to a network port on a computer, router, switch, or another network device. On the other hand, CAT6 (Category 6) is a standard for network cables that provide higher data rates and frequencies compared to its predecessors like CAT5 and CAT5e. Simply put, RJ45 connectors are used to plug CAT6 cables into network devices; CAT6 describes the specifications of the cable itself.